Workstation – Google Custom Search Integration
Brief Overview
Google Custom Search, also known as Programmable Search Engine, enables users to create a search engine for different purposes - their website, blog, or a collection of websites. They can configure this engine to search for web pages in the sites that are added to it.
This integrations connects Workstation with the Programmable Search Engine, to enable users to search for public web pages directly from Workstation's enterprise search.
Capabilities
Search from Workstation for web pages according to your Google's Programmable Search Engine configuration.
Security Overview
The Enterprise Search uses 3rd-party integrations to implement a "federal search". Searches within Workstation are backed by an NLP engine, and a graph database that supports a great user experience.
Workstation Enterprise Search doesn't index 3rd-party data on an independently searchable database.
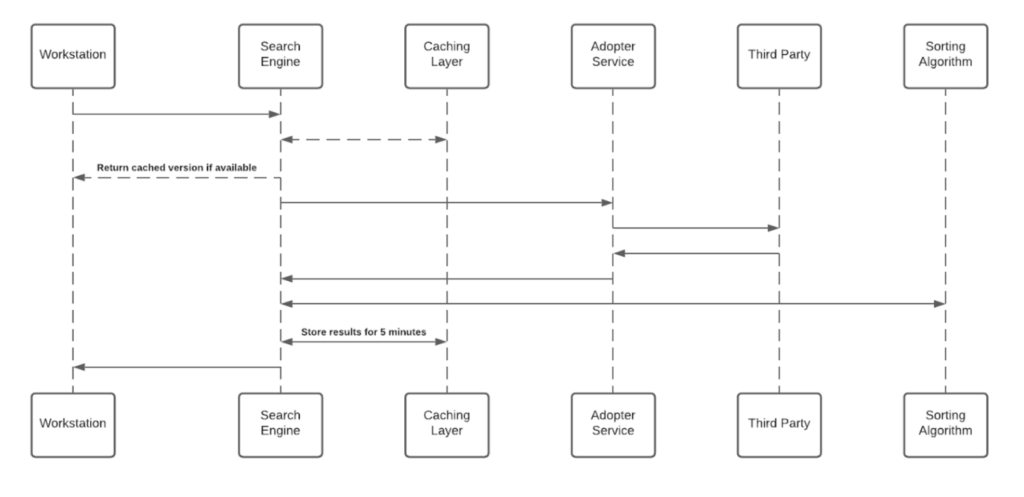
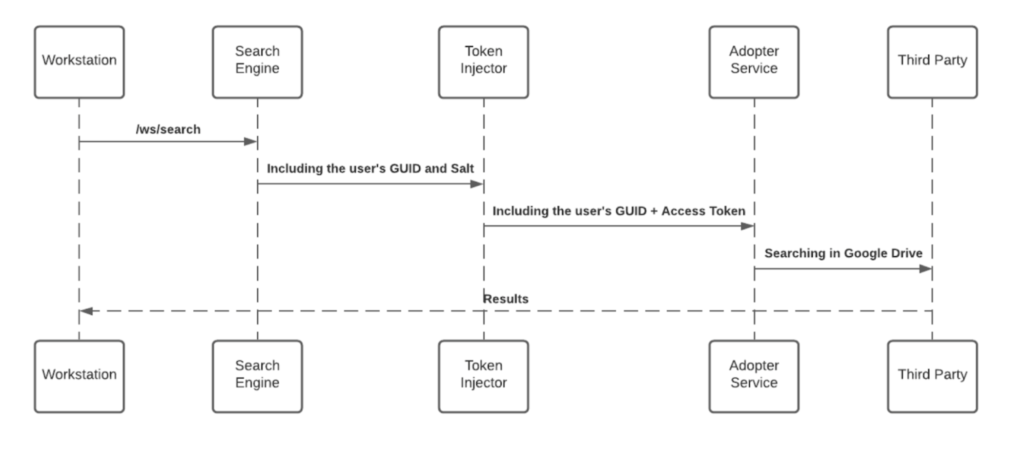
See below sequence diagram describes the searching algorithm:
Notes
- Cache layer saves results for a period of five minutes
- Each Adopter Service creates a unique identifier for the results which is meaningless without access to the 3rd-party and stores it in the graph database
3rd-Party Access and Refresh Tokens
To activate the Enterprise Search (and the Personalized Workspace widgets), each employee is required to grant Workstation permission to access the 3rd-party.
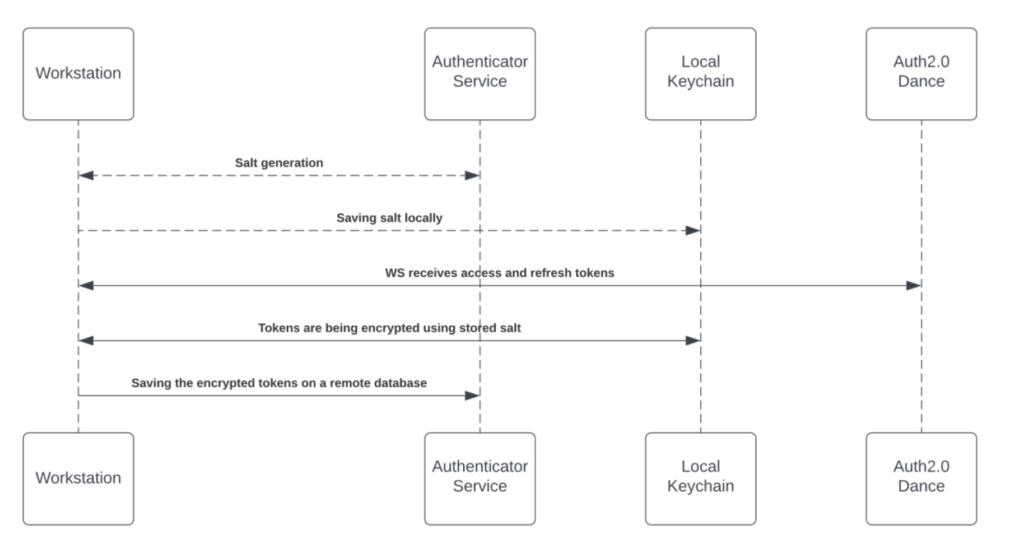
Each time a new access token is granted to the Workstation, the application will encrypt the access and refresh tokens and store it in a remote database.
The encryption process includes a unique private key ("salt") that is generated for each individual at the very first bootstrap and stored in the local machine Keychain.
The salt is irreplaceable and not restorable - losing it causes the access tokens to be voided.
This security measure is being taken to eliminate identity spoofing when accessing high-sensitive data.
See the image below to review the salt generation and storage flow.
Accessing 3rd-Party Content
The third-party apps are being approved and verified by third-parties products.
By the end of the granting process, the third-party apps provide access and refresh tokens that are used by the search engine to establish the requests.
See 3rd-Party Access and Refresh Tokens section above for more information about the storing mechanism.
While searching, the search engine forwards the request, before hitting the Adopter Service, through the Token Injector; a service that injects the relevant tokens to accomplish the request.
The local private key is being handed off over the search HTTPS request for runtime decryption.
JWT Protection
When an end-user initiates a search query - the WalkMe enterprise search starts a search flow that is being protected by a JWT assigned by WalkMe IdP integration, as part of the user signing flow:
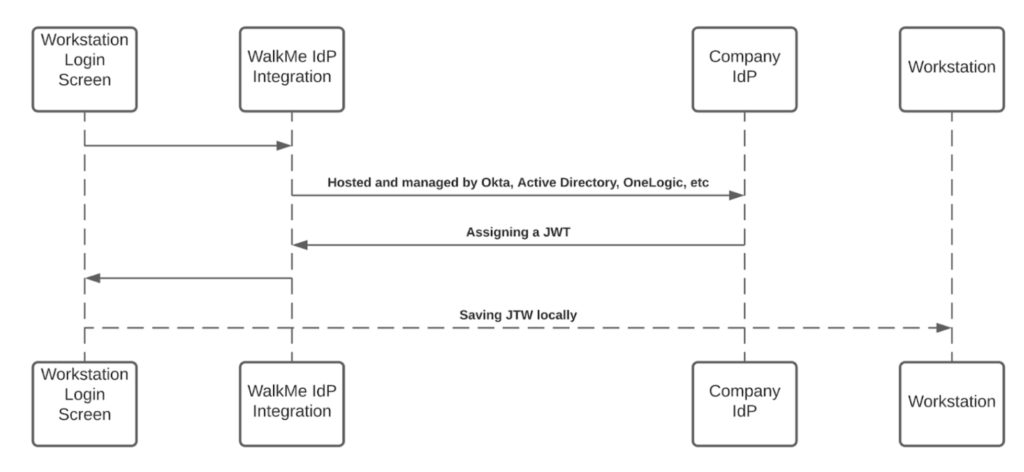
The JWT is proxying the user identity and keeping any HTTPS request secured and individual.
All Workstation requests are protected by a JWT validation.
Create a Programmable Search Engine in Google for Workstation Search
- Go into Google's documentation on Creating a Programmable Search Engine
- Follow the instructions using your Google Account (get an account if you don't have one). In the Sites to search section, add the pages you want to include in your search engine.
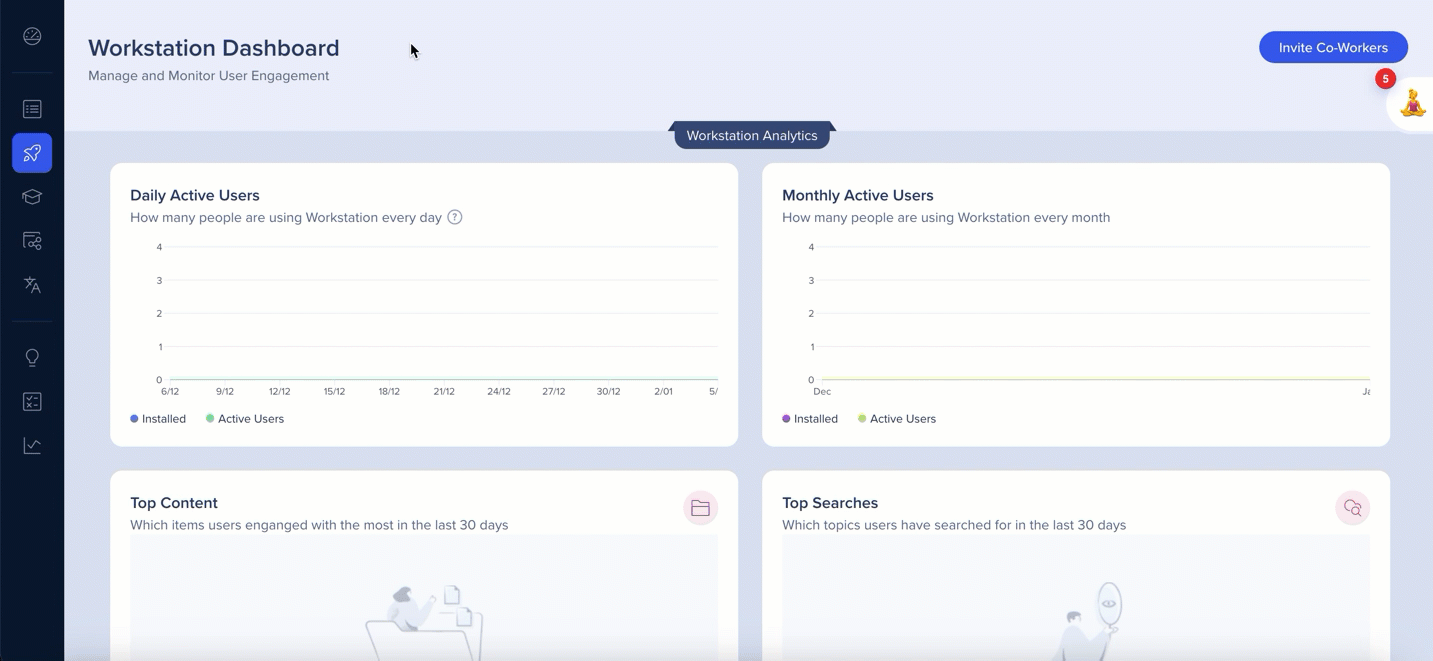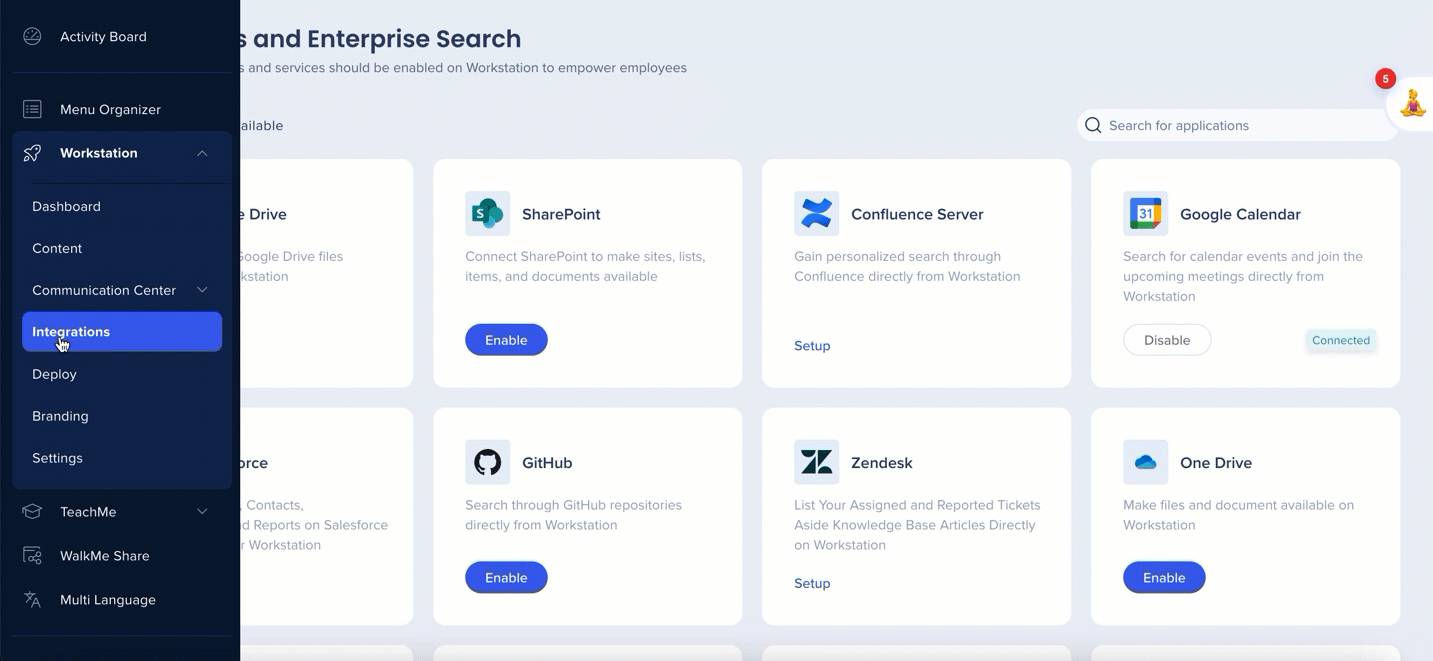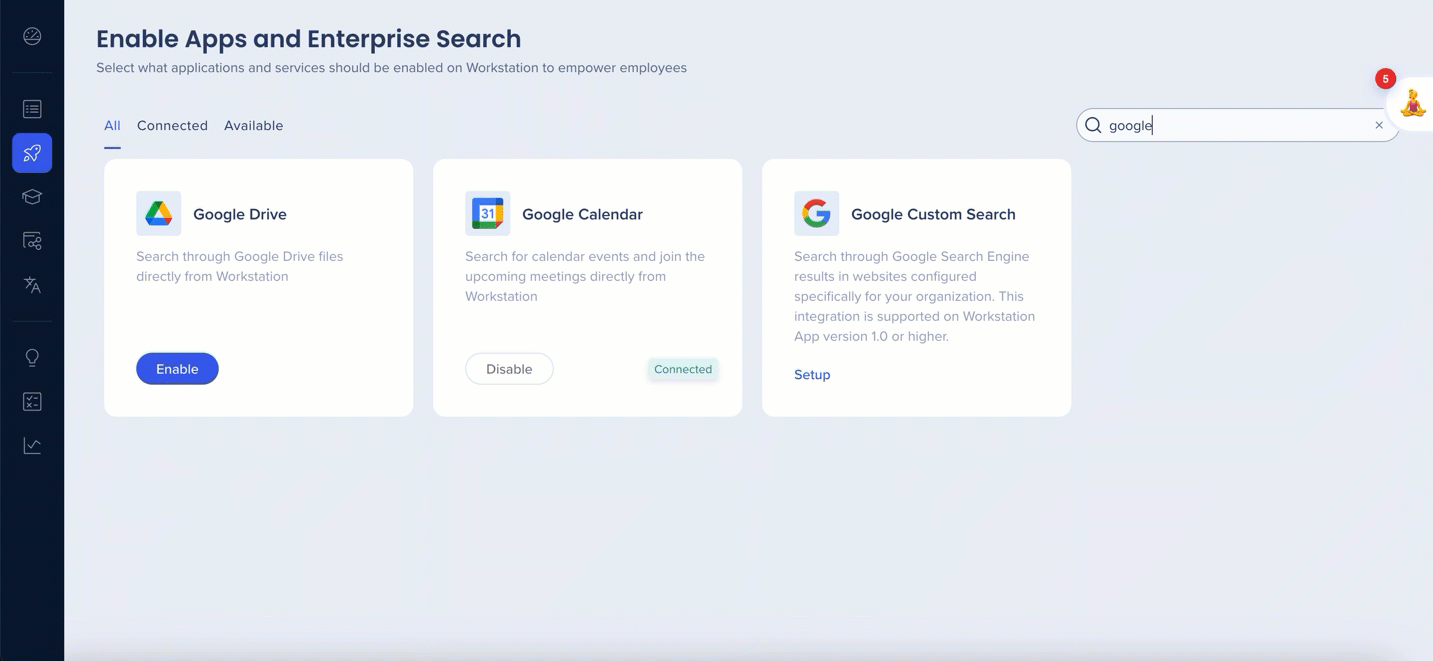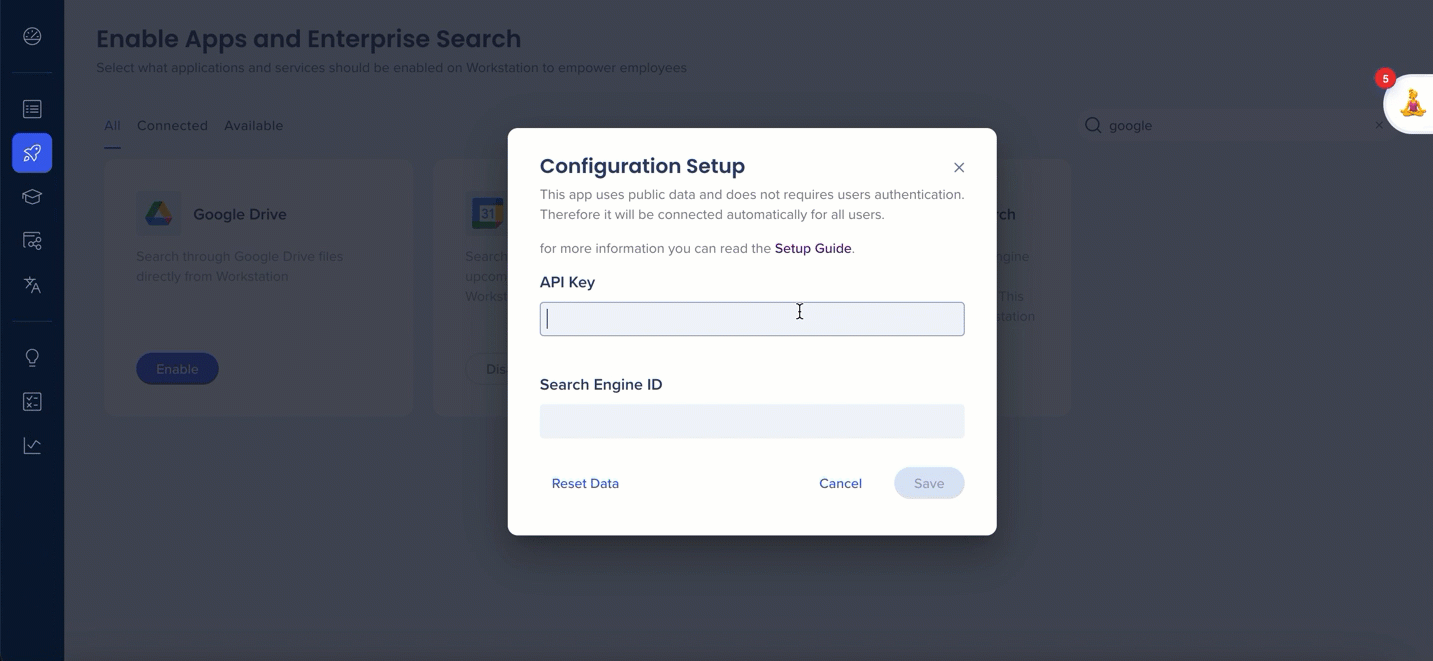
- After creating your search engine, in the Overview screen copy the search engine ID.
- Custom Search JSON API requires the use of an API key. An API key is a way to identify your client to Google. Get a Key by clicking the button in this documentation.

- Copy the API Key.
- Login to Console to configure the parameters copied in the Integrations page.
- The integration will appear in the Integrations tab of the app's Settings
Segmentation
Integrations can be segmented to a sub-set of users and audiences, rather than being enabled for all end-users. This feature streamlines the integration process and helps to ensure that users are only using the integrations that are relevant to their work.
To segment a Workstation integration:
- Navigate to the Workstation Integrations page in the console
- Click the All button on the integration you would like to segment

- Click Select specific recipients in the Manage Access popup
- Select the audiences or individual users from the dropdowns to handpick who can use the integration
- Click Apply