Workstation Enterprise Search
Brief Overview
Workstation Enterprise Search empowers you to discover applications and resources through a comprehensive, unified search experience. It functions as a robust search engine capable of searching for information across both WalkMe content and content within third-party apps that were added through the Console's Integrations page.
Enterprise search does the following:
- Provide fast and efficient knowledge discovery, eliminating the need to search across multiple disparate data sources
- Generate personalized, AI-powered results where users can filter by app and file type
- Preserve business security and end-user privacy, with zero indexing and respecting access permissions
Get to Know
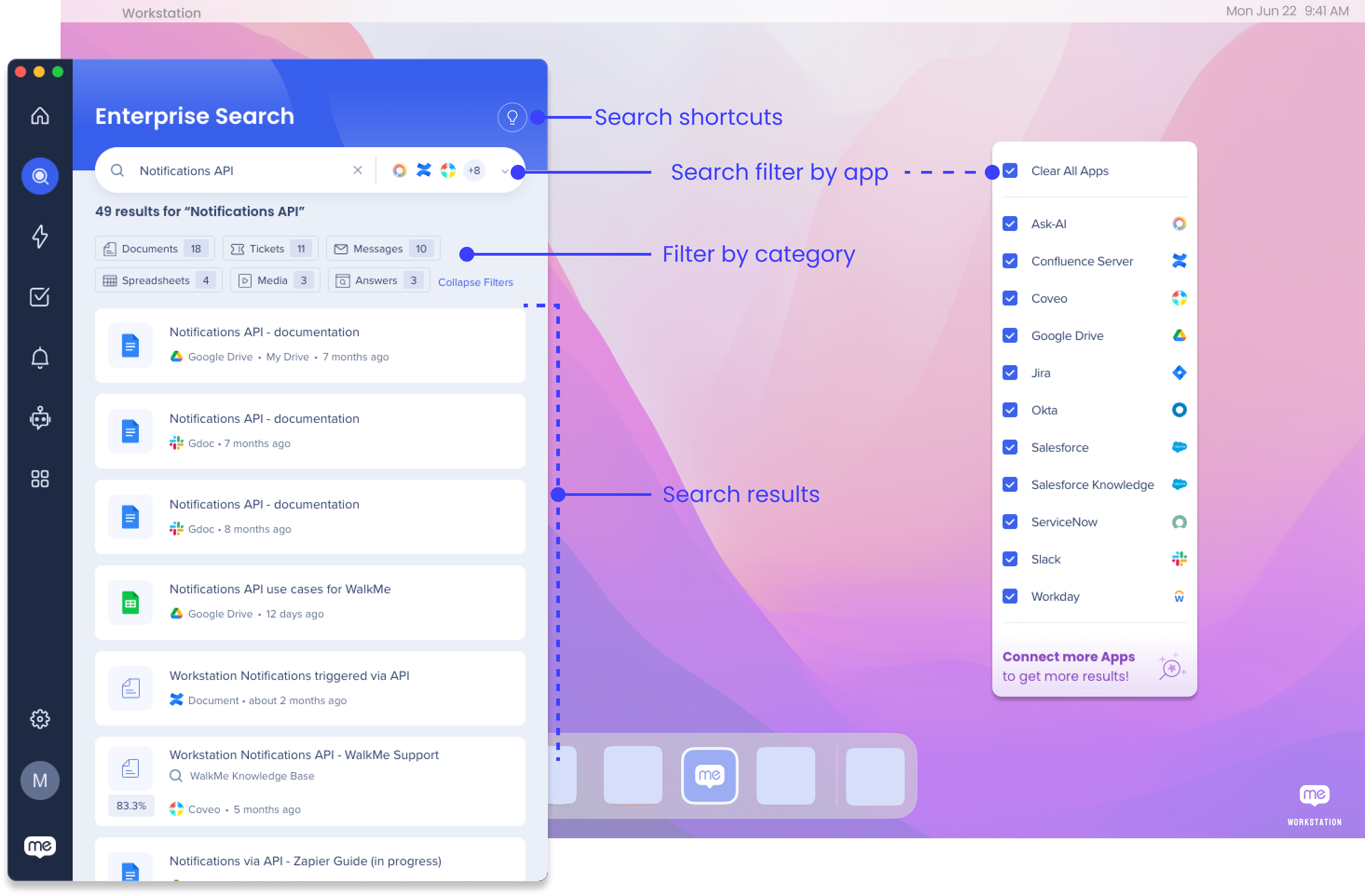
Filter by app
You can search across all of your integrated apps, or filter the search to specific apps:
- Click the dropdown in the search bar
- Select the apps you want to filter the search to
Search Shortcuts
There are also quick keyboard shortcuts you can use in order to adjust your apps without changing the search filter.
- Open search: Press Ctrl/Cmd+F
- Filter your search to a specific app: Type in:{app name}
- For example, if you have all of the apps selected in the filter and then type in:servicenow, you will only see results from ServiceNow
- Remove the shortcut to return to your filter
- Add an app to your search filter: Type add:{app name}
- For example, if you filtered your search to a few apps and you want to add ServiceNow without adjusting your filter, type add:servicenow
- Remove the shortcut to return to your filter
- Remove an app from your search filter: Type remove:{app name}
- For example, if you no longer want to see results for ServiceNow, type remove:servicenow
- Remove the shortcut to return to your filter
Filter by category
When your search results load, there are additional category filters that appear. This lets you further specify your search to the content type.
This comes in handy, for example, if you know you're looking for a document, but you don't remember what app it's from. Simply click the Document button and the search will filter to only documents across all of the apps in your search filter.
The category filter only shows the content type that appeared in the search results. So if none of the results are a document, then the document category won't be a choice.
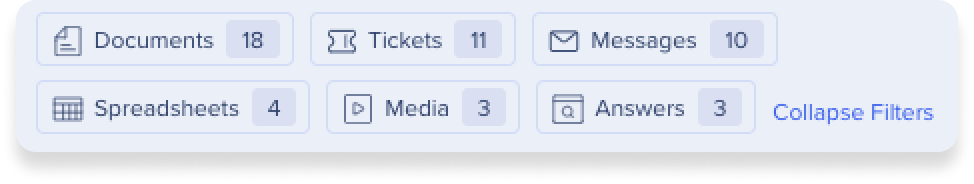
- Document
- Ticket
- Message
- Spreadsheet
- Media
- Answers
- ActionBot
- Resource
- Code
- Deals
- Opportunities
- Accounts
- Events
- Reports
- Apps
- Presentations
- Leads
- Website
Search results
Your search results will show you the content name and what app it's from. Clicking on a result will put it in the Recently Viewed widget on your homepage so that you can quickly get back to it.
Auto-correct
Users no longer need to worry about precise spelling or exact matches. Our search capability will intelligently understand their intent and provide the most relevant results, even if there are minor errors or misspellings in the search query.
Here's how it works:
- Open-source library (non-AI): An open-source library will fix common grammar and vocabulary mistakes in search queries. Open-source library autocorrections supports English only.
- OpenAI integration: The integration with OpenAI will take search query corrections to the next level using AI-based algorithms. OpenAI autocorrections supports all languages.
Sorting search results
Results sorting flow
The Enterprise Search uses a Sorter Service that sorts the results according to its relevance. How the sorter service performs the sorting:
-
A user searches for a term in the Workstation app
-
Search service gets the term and calls for each connected app's service in real time
-
Connected app's service search for this term, each with its own API call and implementation
-
Search service gets all the search results from all the connected apps
-
Search service calls the sorter service with the results
-
Sorter service sorts/orders the results and sends the sorted/ordered results back to the Search service
-
Search service returns the results back to the Workstation app
Sorting scoring methods
The Sorter service uses 9 different scoring methods, including stemming, fuzziness and NLP, in addition to the basic Levenshtein distance. Each results gets gets 9 scores (one per method), ranging from 0 to 1, in order to set the prioritization.
-
LevenshteinFast: Computational algorithm used to calculate the Levenshtein distance between two strings, which is a measure of the minimum number of single-character edits (insertions, deletions or substitutions) required to transform one string into the other
-
JaroWinkler: String similarity measure that is used to compare the similarity between two strings
-
IdenticalTokens: Grants a score based on relative number of identical words (tokens)
-
IdenticalTokensStemmed: Grants a score based on relative number of identical stemmed words (tokens) - stemming is the process of removing ing, ed etc. from a word in order to get its most basic form
-
Stopwords: Grants a score based on the relative number of identical words (tokens) while ignoring stop words (if, and, or etc.)
-
Fuzzy: Grants a score for similarity of 2 strings while taking typos into consideration
-
RequestKind: Describes the type or category of a request made by a user (Currently not in use)
-
TimeRelevancyStart: a function that scores search results based on their recency, giving a higher score to more recently edited/created documents. It grants a score according to the time difference (days) between now and the result's last edit/create date. This function only works if the app's API supports it, like in Google Drive
-
TFIDF (Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency): It is a numerical statistic that reflects how important a word is to a document in a collection or corpus. It calculates a score based on the frequency of the word in the document and the rarity of the word in the entire collection. This method is only used and effective when searching for phrases with more than two words
Other sorting conditions
The sorter in Workstation gives priority to the following results in the search:
-
Recently Viewed: Items that were recently viewed by the user get a higher prioritization in search results, since they're most likely to be more relevant to the user during the search process
-
Apps (from IDP integrations like Okta): When there is a 100% match between the search query and an app result, it will receive higher priority
-
Native sorting: Results from the following applications give prioritization to the order of results received from API's and leverages the 3rd parties prioritization capabilities to display similar order to native applications
-
Confluence
-
Jira
-
-
Resources: In cases where there are results containing both WalkMe content and integrations, and no results have a 100% match, the resources results will be prioritized. Two resources are displayed on top of the search results
Search by keywords
Our entry algorithm generates entries for each WalkMe item based on their title and keywords.
-
If an item has no keywords, only one entry is created using its title
-
If an item has keywords, additional entries are generated for each keyword including the title and the keyword itself
Each entry is scored based on its relevance to the search query, and the results are displayed accordingly. To increase the chances of an item appearing in search results, it's important to have keywords that closely match the search terms. However, keywords are not considered word-by-word, but as a whole. Therefore, long keywords should be split into logical groups or terms.
-
For example,
"career development learning training advice information help system"would be better split as"career development", "learning system", "training system" -
Note that an exact match is not required. For instance, an item with the keyword
musiccould still appear in search results for the termmusician
Separating each possible word as a keyword can harm the search results.
-
For instance, the keyword
“career development learning training advice information help system"will match with terms like"legal advice", "onboarding system", "vacation help", and so on, if each word is considered as a separate keyword. Therefore, it's better to be more precise as mentioned above to reduce false positives while still making it useful for partial searches
Indexing
Workstation does not index results. Some data is stored on the client side. For example, the data which appears on Recent Search Results or in the Recently Viewed widget.
Rest of the data displayed to the user on the Search flow is brought in real-time from the 3rd-party apps API's.
Integrations
The Enterprise Search uses 3rd-party integrations to implement a “federal search”. Searches within Workstation are backed by an NLP engine, and a graph database that supports a great user experience. Workstation Enterprise Search doesn't index 3rd-party data on an independently searchable database. See below sequence diagram describes the searching algorithm:
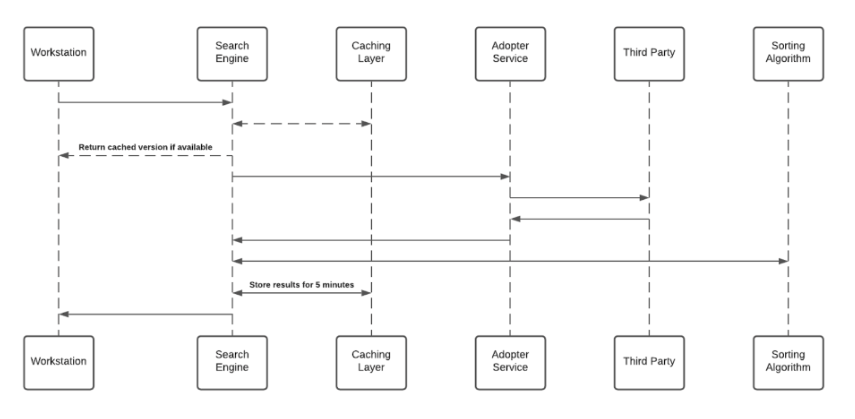
- Cache layer saves results for a period of five minutes
- Each Adopter Service creates a unique identifier for the results which is meaningless without access to the 3rd-party and stores it in the graph database
3rd-Party Access and Refresh Tokens
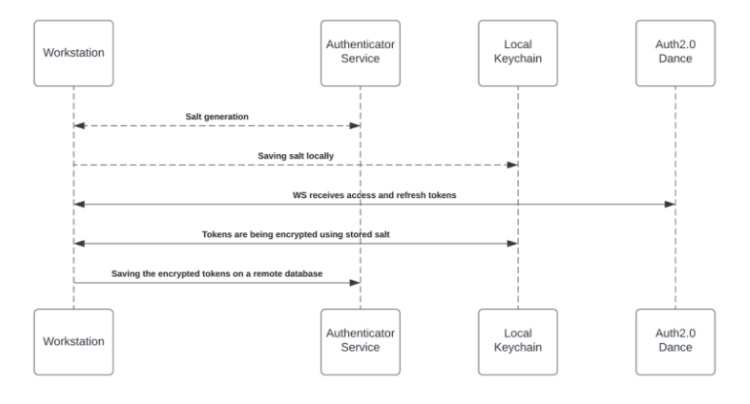
To activate the Enterprise Search (and the Personalized Workspace widgets), each employee is required to grant Workstation permission to access the 3rd-party. The granting process is using the OAuth2.0 protocol. Each time a new access token is granted to the Workstation, the application will encrypt the access and refresh tokens and store it in a remote database.
The encryption process includes a unique private key (“salt”) that is generated for each individual at the very first bootstrap and stored in the local machine Keychain. The salt is irreplaceable and not restorable – losing it causes the access tokens to be voided. This security measure is being taken to eliminate identity spoofing when accessing high-sensitive data.
See the diagram below to review the salt generation and storage flow.
Accessing 3rd-Party Content
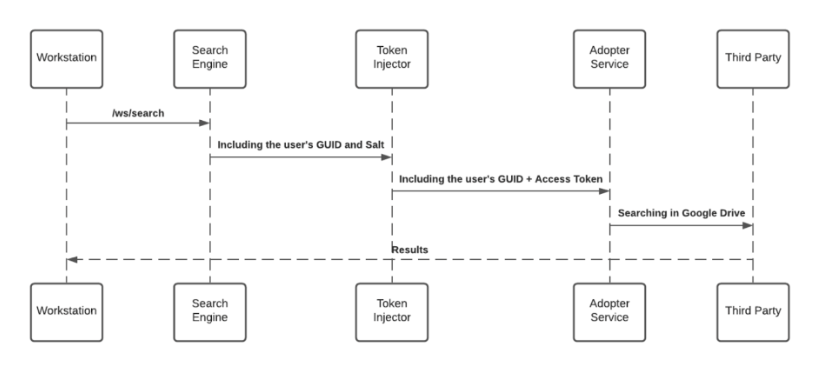
Accessing 3rd-party content requires user consent, and in some cases, mostly on Microsoft products, an organization admin consent. Users grant Workstation the necessary permission by approving an OAuth2.0 consent screen that is being triggered by them from the Workstation application (“Third-party apps”).
The third-party apps are being approved and verified by third-parties products. By the end of the granting process, the third-party apps provide access and refresh tokens that are used by the search engine to establish the requests.
See 3rd-Party Access and Refresh Tokens section above for more information about the storing mechanism.
While searching, the search engine forwards the request, before hitting the Adopter Service, through the Token Injector; a service that injects the relevant tokens to accomplish the request. The local private key is being handed off over the search HTTPS request for runtime decryption.
JWT Protection
When a user initiates a search query – the WalkMe enterprise search starts a search flow that is being protected by a JWT assigned by WalkMe IdP integration, as part of the user signing flow:
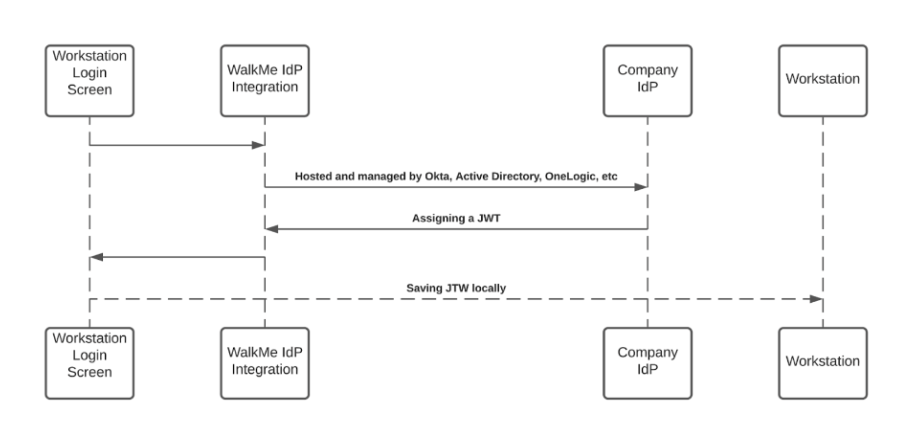
The JWT is proxying the user identity and keeping any HTTPS request secured and individual.
All Workstation requests are protected by a JWT validation.
Read more about integration security here.
Fuzzy Search
Fuzzy Search provides an auto-correction to search queries. The search intelligently understands users' intent and delivers relevant results, even if there are minor errors or misspellings in the search queries.
We support two options for auto-correct:
Open Library Auto-Correct
- Configuration required? No, it works on default for all systems
- Language Limitations: English only
- Characters number: 3 or more
AI-Based Auto Correct
- Configuration required? Yes, OpenAI Integration should be configured in Console
- Language Limitations:All languages
- Characters number: 10 or more (this is in order to effectively use the API Calls to OpenAI and reduce costs)
Avoid wrong search fixes
If users correct an expression for 3 times or more, it will avoid fixing it for the future. That is in order to prevent scenarios as following-