Brief Overview
Logic rule allows you to create logic statement in the Rule Engine based on dynamic text attributes and predefined constants, to compare fields including: dates, numbers, and monetary values by using arithmetic expressions.
Use Cases
- Date comparison
- Monetary value comparison
Here are some in depth examples of the way you might use logic rules in a solution:
Trigger a ShoutOut close to a due date
You can use a logic rule to trigger a ShoutOut in the final days before a due date, to remind users that the deadline is coming up and encourage a final effort.
To do so:
- Create an attribute called DueDate
- Create the following Logic Rule - @DueDate - today <= 5days

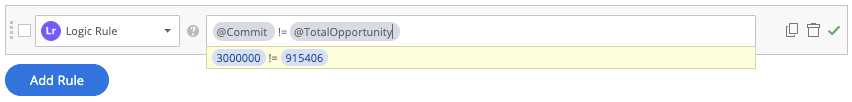
Check if the commit value is equal to the total opportunity value
You can use a logic rule to easily compare numbers and see if the commit value is equal to the total opportunity value.
- Create dynamic text attributes for both fields - Commit & Total Opportunity
- Create the following logic rule - @Commit != @TotalOpportunity
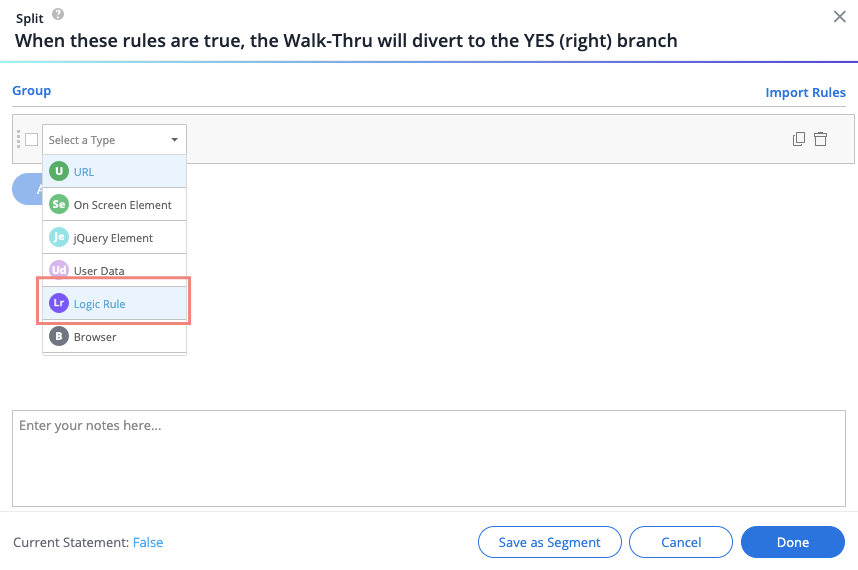
How to use a Logic Rule
- In the Rule Engine, select Logic Rule from the dropdown list
- Enter your logic statement in the highlighted field
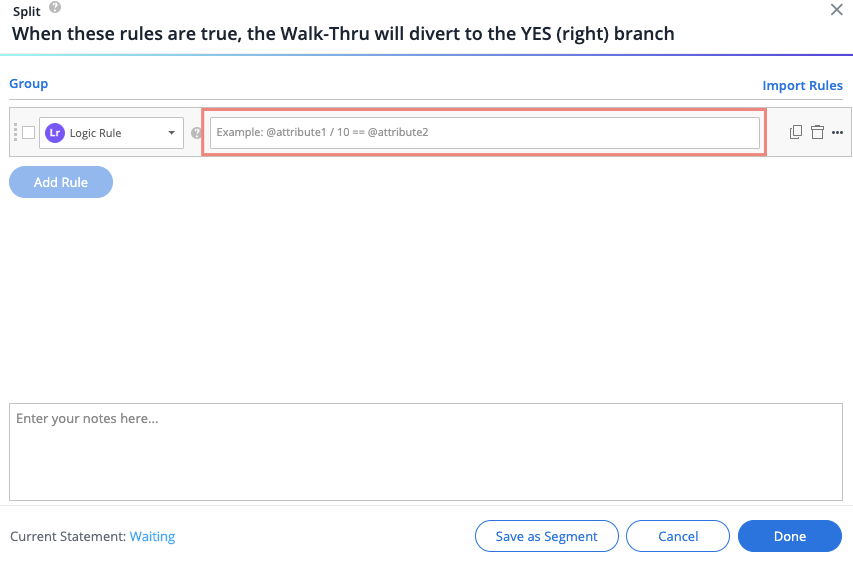
How to Create a Logic Statement
A logic rule should be written in the form of an equation/in-equation, for example:
- @Date1 - Today < 10Days
- @Attribute1 + @Attribute2 == @Attribute3
While creating the logic rule, a preview bar will display the values in the dynamic fields as long as they appear on the webpage that is connected to the editor at that time.

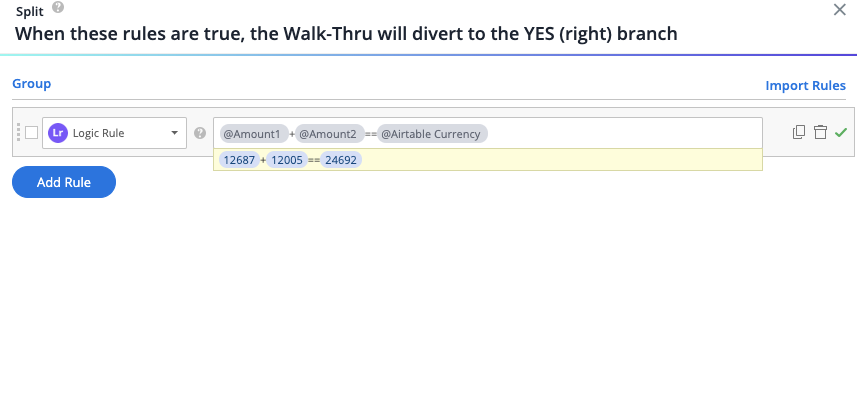
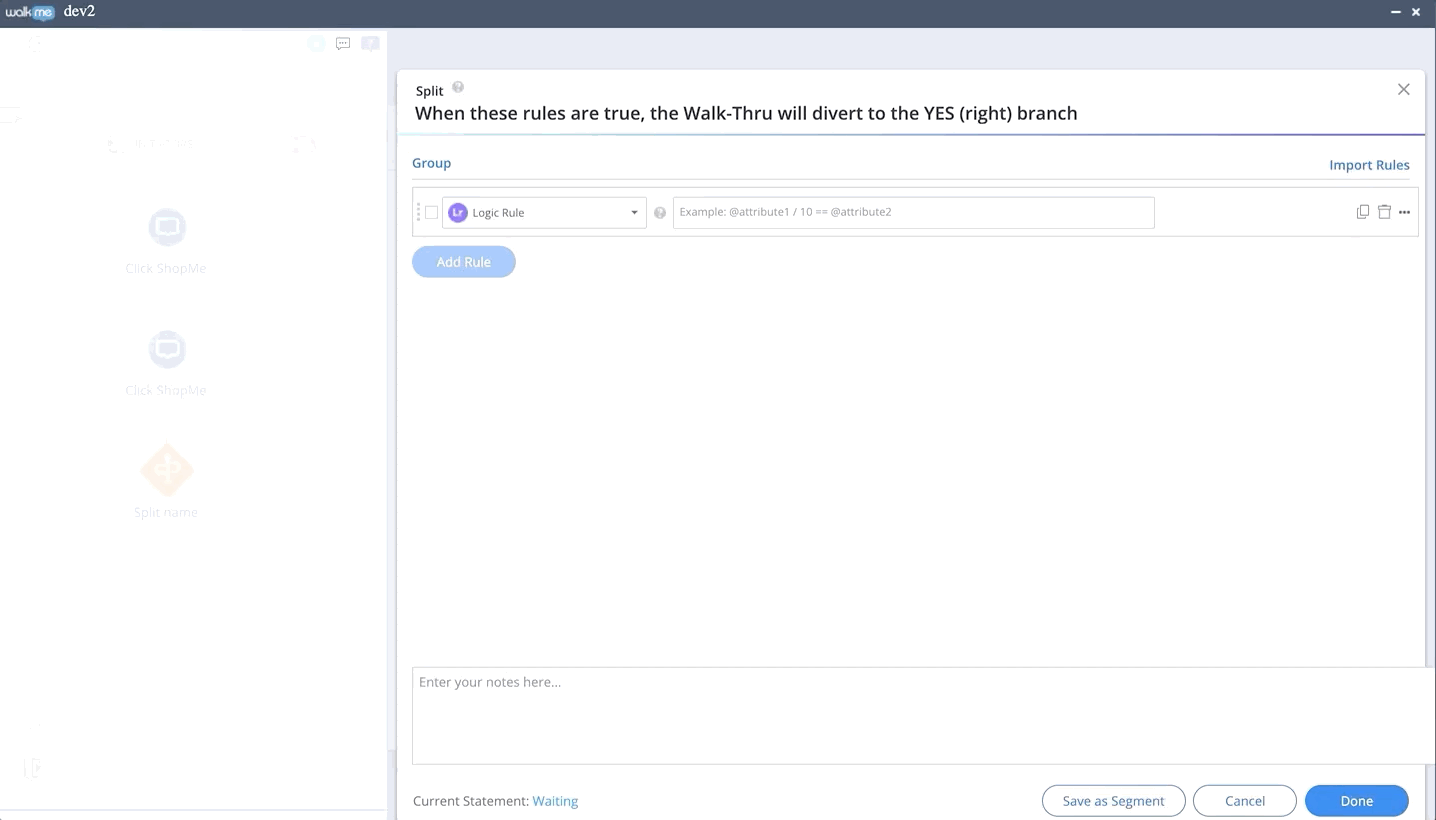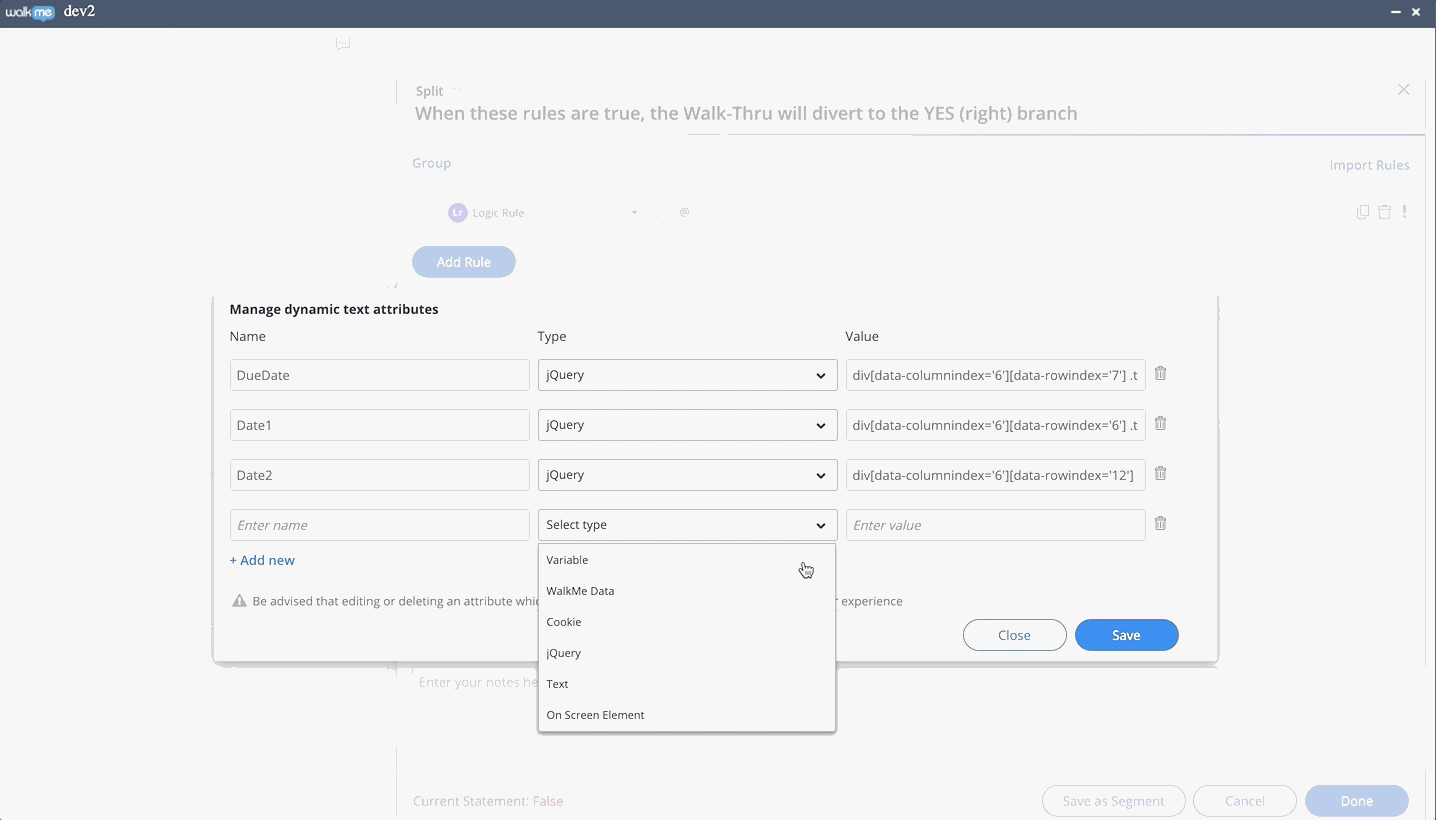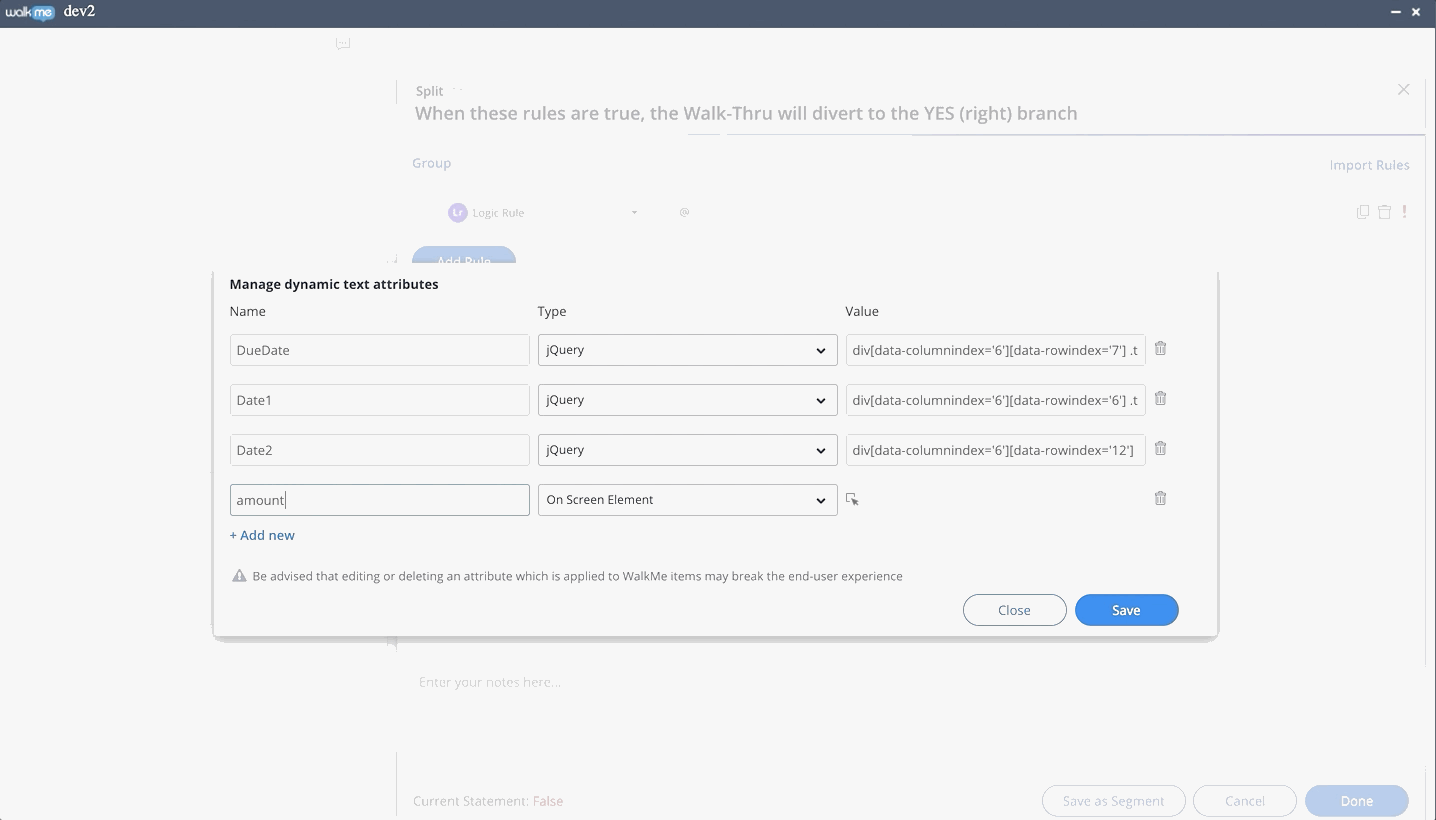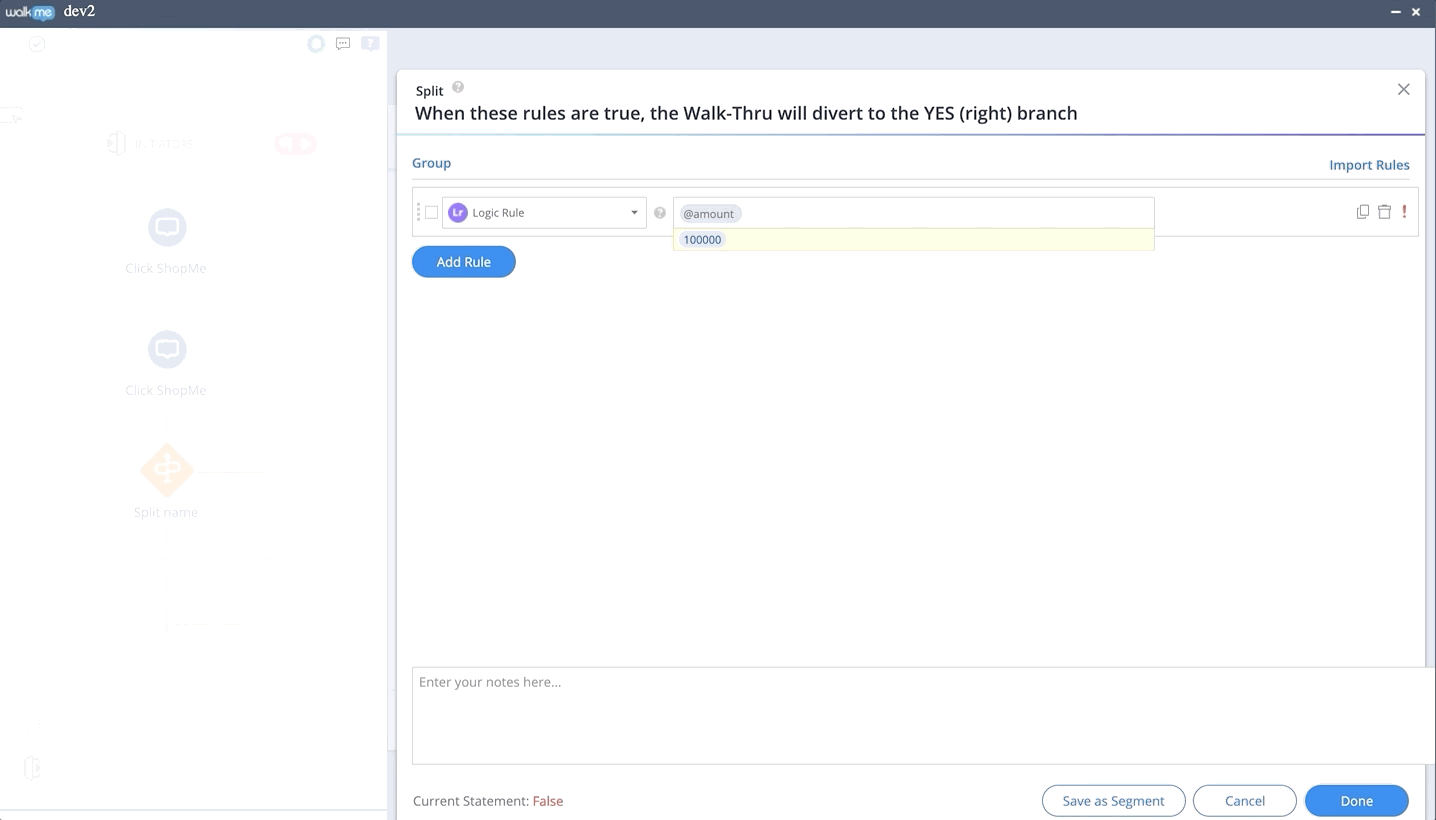
Using Dynamic Text Attributes
- To add an attribute, simply type @ and choose an attribute from the dropdown list
- You can begin typing the attribute name to filter the list
- You can add as many attributes as you want
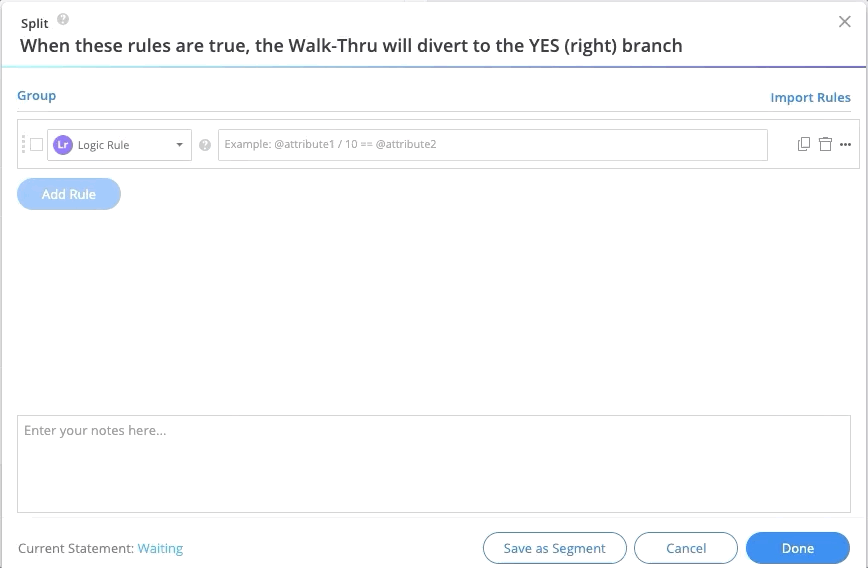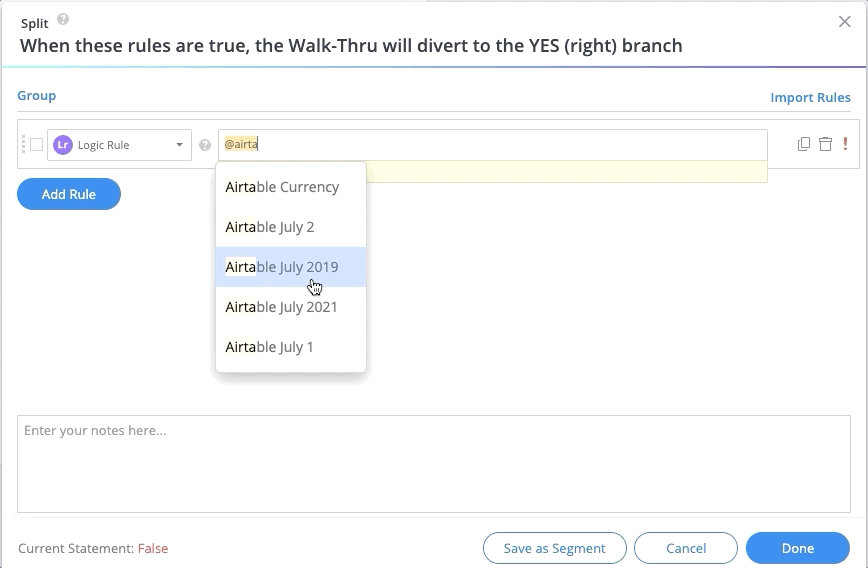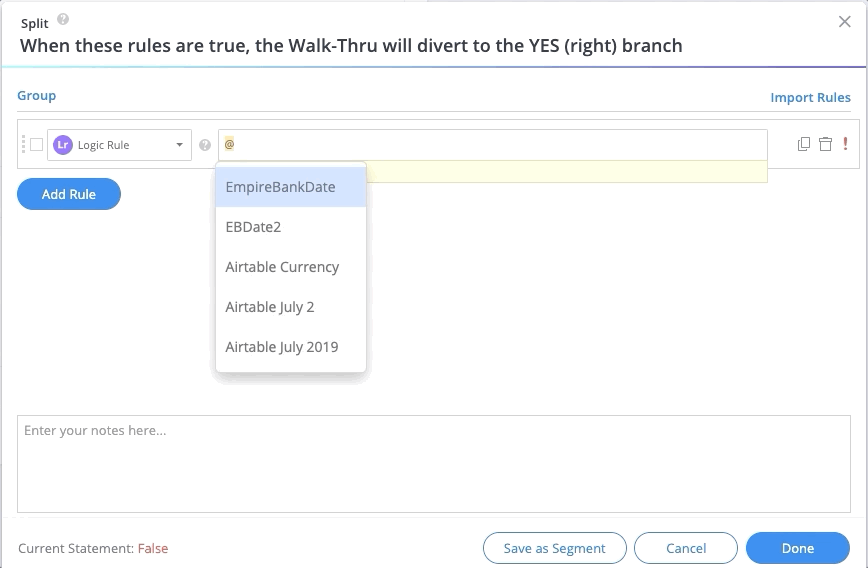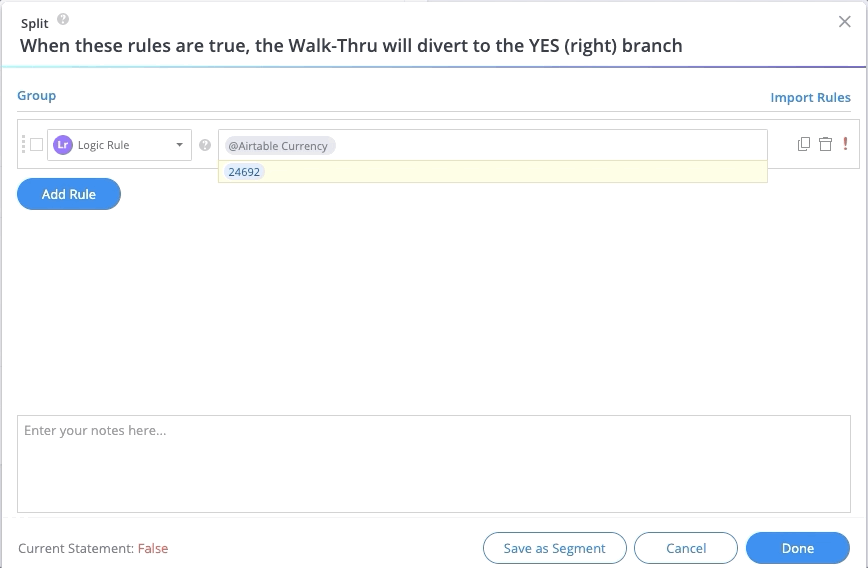
- It is also possible to create new and manage existing attributes directly from the Rule Engine when using the logic rule
Using Dynamic Text Attributes with Static Text Values
Attributes with static text values can be created and used for the comparisons in logic rules.
Example:
@dateTest is the on screen element with a date and @absoluteDate is the static date value.
The builder can now compare the dynamic date on the screen with a predefined date of their choosing.


Using a Predefined Constant
Simply type one of the following constants:
| Constant |
Remarks |
| second |
Can also use "seconds" |
| minute |
Can also use "minutes" |
| hour |
Can also use "hours" |
| day |
Can also use "days" |
| year |
Can also use "years" |
| today |
Returns today's dynamic date, for example - 30/07/2020 |
| now |
Returns today's dynamic date & time, for example - 30/07/2020 18:30:45 |
Note:
- Capitalization doesn't affect constants
- You can multiply constants by typing a number next to the constant, for example - 10day, 2year, etc.
Using Arithmetic Actions, and Comparison
You can use arithmetic actions to add, subtract, divide or multiply attributes. For example:
@Att1/12
@Att2*Att3
@Att4+@Att5
@Date1-today
To compare sides of the equation, use one of the following symbols:
| Symbol |
Meaning |
| == |
Equal |
| != |
Not Equal |
| > |
Greater than |
| >= |
Greater than or equal to |
| < |
Less than |
| <= |
Less than or equal to |
Technical Notes
-
We support a number of apps where we can identify the date format and convert it for correct comparison. WalkMe would first check if you are capturing the date in one of these apps. These apps are:
-
SAP Concur
-
Microsoft Dynamics
-
Salesforce Lightning
-
If you are using date comparison in a different app, WalkMe will take the format from the browser's locale
-
If the builder knows the format their users are using, they can choose to define the format in the dynamic attribute settings. This will override the browser's locale.
- Standard date formats are supported: mm/dd/yyyy, mm.dd.yyyy, etc.
-
- 29/NOV/2024
- 29/Nov/2024
- 29/november/2024
- 29/November/2024
- 7/mar/1989
- 07/mar/2024
- 7/MARCH/2028
- When logic rules encounter a string that is a combination of text and a number, it will extract the first number from the string (logic rules don't support text - only text based dates - see above)
- When using a jQuery selector as a dynamic attribute, you must pick up the direct element that holds the text, rather than any of its ancestor elements
- Certain date fields in Workday® are not supported since they are broken into 3 elements
- . Use attributes to enter any type of value (date, number, text)
- Data that is saved using the ActionBot is currently not supported in logic rules (because it is saved in the form of an object to be used in a Smart Walk-Thru).
-
The largest number that can be precisely represented is 9007199254740991. Every number above that will be "rounded" to a 16 digit number plus zeros.
For example: 123456789123456789123 will be converted to 123456789123456800000
- Logic rules cannot evaluate dates prior to 01/01/1970
Troubleshooting
- When using OSE -
- The format of the date in the website should match the builder's local (which implies a date format). If it doesn't, the logic rule might show "invalid date"
- Example: On ynet, an Israeli site, you will see dates in en_IL local (format will be DD/MM/YY - note where the D and the M are). As a builder, I use an attribute based on an on screen element in the logic rule. But, my own browser is set to en_US. If the date was 23/2/22, the logic rule will show "invalid date" as it assumes the local is US which should give a US format (MM/DD/YY). Considering there isn't a 23rd month in the year, the error shows.
- If there isn't a gap between the site's date format and the builder's browser local, all should work well - WM will check the end-user's browser local while running (in published environment), and will "understand" how to read the date
- Example: On screen element holds this date: 3/4/22. Is it March or April? WM "decides" based on the end user's browser local.
- Using fixed/absolute date (text type attribute) -







