Welcome to the
WalkMe Help Center
Please log in to continue

Please log in to continue

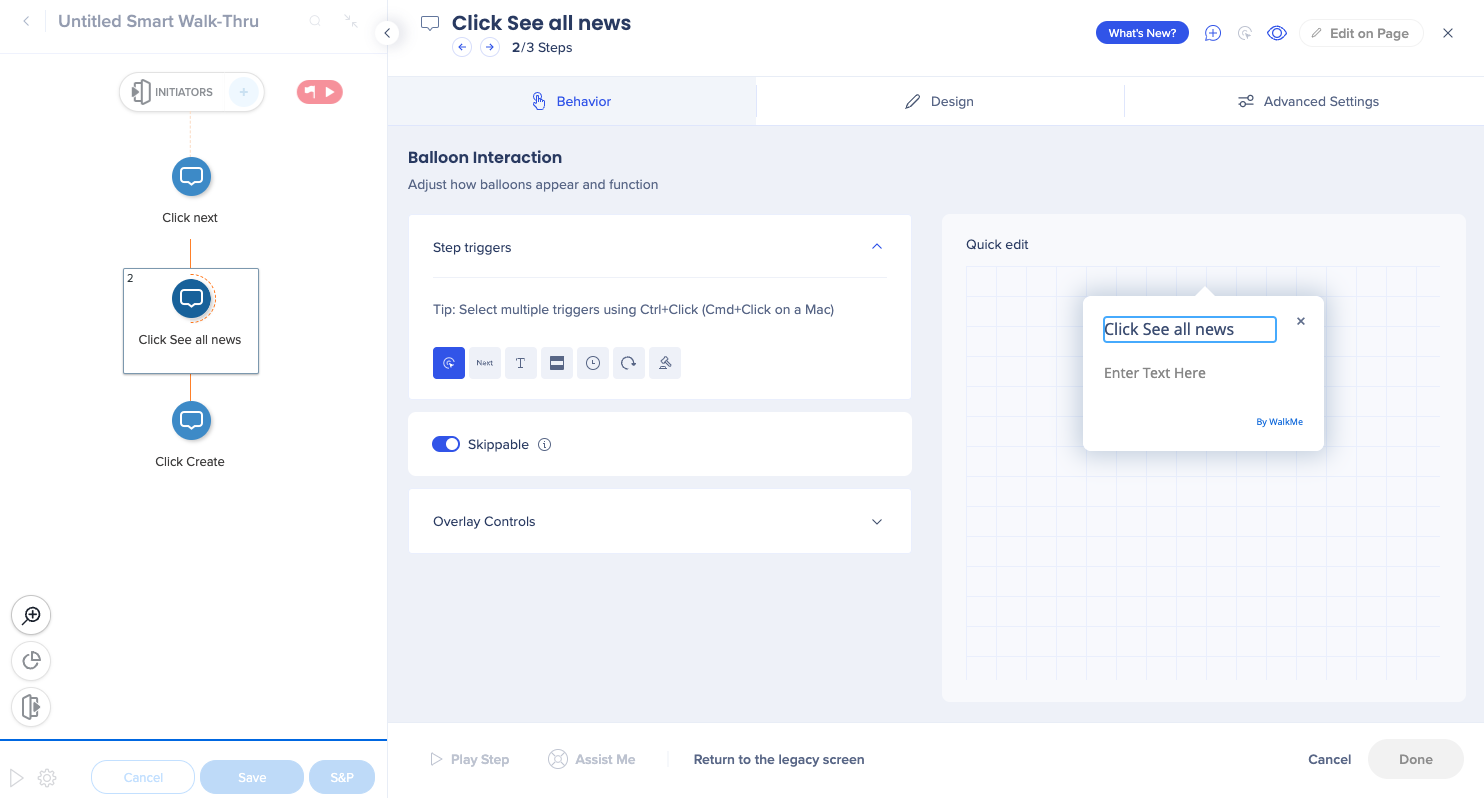
Skippable steps let Smart Walk-Thrus continue when a step's target element is not found. By marking a step as skippable, you ensure that the flow progresses smoothly even when elements appear conditionally or vary by user role.
This article explains how skippable steps work, when to use them, how to configure them, and how they behave in complex flows.
Consider a form that behaves differently based on country selection:
By marking the step that targets the State field as skippable, the Smart Walk-Thru continues regardless of which country is selected.
In process-oriented solutions, not all elements are always present on the page. This can happen when:
When a Smart Walk-Thru reaches a step whose element cannot be found:
You can apply the Skippable setting to element-oriented steps, including:
To mark a step as skippable:

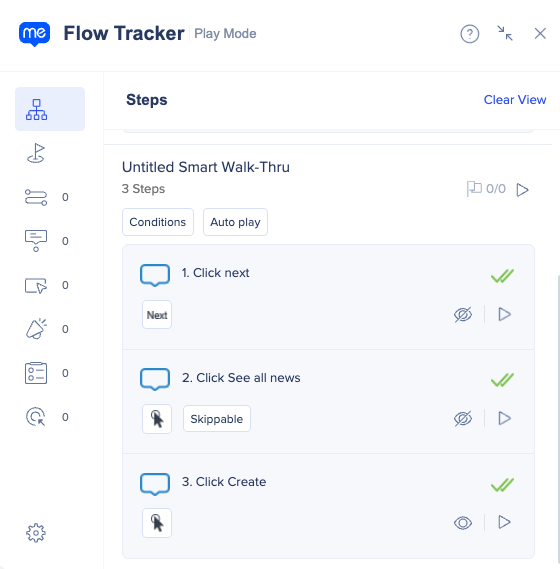
In the flow map, skippable steps are indicated by a dotted semi-circle icon.
Peer steps can cause users to get stuck if no triggers are available to advance the flow.
When the main step in a group is skippable and its element is not found:
Triggers can be added to peer steps using BBCode.
Flow Tracker displays an indication when steps are skipped during a Smart Walk-Thru. This lets you verify that skippable behavior occurred as expected during playback.